After googling this topic, I used to think it’s easy to flash the firmware to an ESP-12/12E, just connect the wires and simply click will do it. However I encountered some problems and I managed to solve it. So I write this post to share my experience.
My NodeMCU firmware is built on http://nodemcu-build.com/
After flashing with esptool / nodemcu_flasher from bbs.nodemcu.com / official ESP8266 Flash Tool, the ESP-12E could not boot normaly, I got outputs from baudrate 115200 or 74880 such as:
Fatal exception 28(LoadProhibitedCause):
epc1=0x40224847, epc2=0x00000000, epc3=0x00000000, excvaddr=0x03001581, depc=0x00000000
ets Jan 8 2013,rst cause:2, boot mode:(3,0)
load 0x40100000, len 29804, room 16
tail 12
chksum 0x4a
ho 0 tail 12 room 4
load 0x3ffe8000, len 2208, room 12
tail 4
chksum 0xb7
load 0x3ffe88a0, len 8, room 4
tail 4
chksum 0xfb
csum 0xfb
don't use rtc mem data
or
Fatal exception 0(IllegalInstructionCause):
epc1=0x40210354, epc2=0x00000000, epc3=0x00000000, excvaddr=0x00000000, depc=0x00000000
ets Jan 8 2013,rst cause:2, boot mode:(3,0)
load 0x40100000, len 29804, room 16
tail 12
chksum 0x4a
ho 0 tail 12 room 4
load 0x3ffe8000, len 2208, room 12
tail 4
chksum 0xb7
load 0x3ffe88a0, len 8, room 4
tail 4
chksum 0xfb
csum 0xfb
don't use rtc mem data
It’s something like this post, maybe it’s not enough to flash firmware to 0x00 and esp_init_data_default.bin to 0x3fc000. What I know is that the chip can’t boot.
After few days, I had an idea. I grabbed an NodeMCU Dev Board, and used esptool’s read_flash command to dump the 4 MByte flash:
$ sudo esptool.py --port /dev/ttyUSB0 read_flash 0x00 4194304 4m.bin
# 4194304 = 4*1024*1024 4MByte
And, I successfully flashed it to an ESP-12E module by official ESP8266 Flash Tool with the config
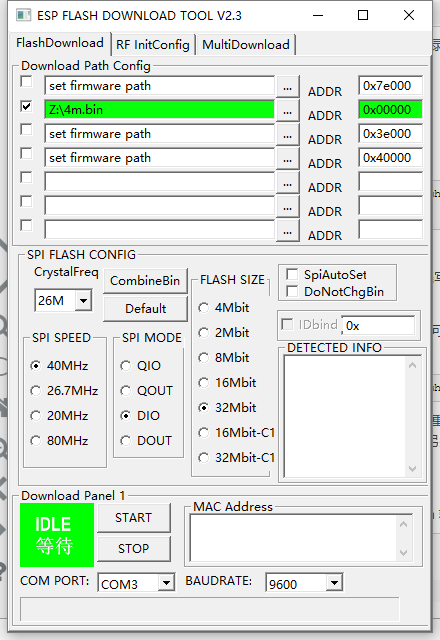 After a restart, try using 115200 baudrate to connect it. And everything seems good.
After a restart, try using 115200 baudrate to connect it. And everything seems good.
At last of this post, is my hardware connections and the 4MByte flash dump file. Make sure that GPIO0 is low if you want it to boot flash mode and high(or float) for normal mode.
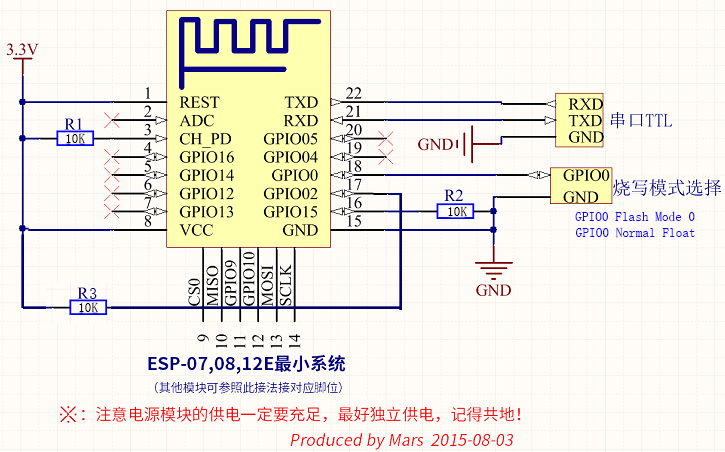
4MByte binary file: 4m.7z
================== Below is the Chinese version =======================
本来以为刷个ESP-12E很简单的,但是我刷了就不行,后来找了个NodeMCU把它的flash整个读取了再整刷编程器固件就好了。
后来做了个用GPIO0做输出的电路,但是之后发现容易导致GPIO0电平不对(GPIO0有连外部电路,开机时GPIO0大约只有1.7V,导致无限进入刷机模式,后来把外部输出换了,GPIO0悬空,开机时就变回高电平了)。感觉GPIO0、2、15还是不要乱来比较好。
================================================================
Later I encountered a problem like
“boot mode:(7,7)
waiting for host”
And the solution is that make sure GPIO15 is LOW, instead of float.
 After a restart, try using 115200 baudrate to connect it. And everything seems good.
After a restart, try using 115200 baudrate to connect it. And everything seems good.