最近在学习数据结构,真的是不简单。看到这篇文章,简单易懂,转载下来给自己回味。原文:http://bbs.ahalei.com/thread-4419-1-1.html
最近在学习数据结构,真的是不简单。看到这篇文章,简单易懂,转载下来给自己回味。原文:http://bbs.ahalei.com/thread-4419-1-1.html

前几天用scapy写了个用于802.1x认证的小程序。写完了回顾一下,虽然花了自己两天,但是其实是相当简单的。
今天找了一下,发现 http://blog.csdn.net/wang_walfred/article/details/40044141 一文,对入门非常有帮助。如果当时看了,至少能少耗一天呀。
在这里补充一下我的一点心得。
我的开发是从抓包开始的。抓包之后,就可以通过
pkts = rdpcap('xxxx.pcap')
读取,读取之后就可以用类似列表的办法如 pkgs[1] 来操作特定的数据包。
下面是一些命令:
hexdump(pkt) #have an hexadecimal dump pkt.command() #return a Scapy command that can generate the packet pkt.show() #for a developped view of the packet
其中 pkt.command() 可以返回一个string,运行就可以生成相应的packet,之后的修改就很方便了。
最后的心得是sniff:
sniff(filter='your filter', prn = lambda x: x.show()) # -> list of packets
可以调用prn指定的函数对过滤到的包进行处理。
本人所在学校的IPv6因为各种原因(好吧其实是因为我不懂),默认情况下只能让路由器获得正常的IPv6访问,又或者是不用路由器直接接PC,PC可以正常使用IPv6。使用了路由器,下面的设备可以获取IPv6地址,可以通过IPv6 Ping通路由器,然而不能访问外网的IPv6地址。
尝试过各种方案,如已经被OpenWRT抛弃的6relayd,还有ndppd和北邮的napt66(insmod之后路由就重启了),均失败。最后只能在路由器上架设代理,PC通过代理才勉强解决。
今天偶然得知:ip6tables可以NAT IPv6,而且是相当久之前的功能了,怎么我之前就不知道呢 (;´д`)ゞ
好了进入正题。
首先我们需要在基于OpenWRT的路由器上安装两个kernel modules: kmod-ip6tables 和 kmod-ipt-nat6,如果提示内核版本不对,刷固件换内核吧。(自己编译固件就没这样的问题)
之后,运行
ip6tables -t nat -L
如果有输出就说明NAT表可用。
然后,在开机启动脚本上添加一行
#有人说这样比较不优雅,其实也可以直接改LAN的配置 ifconfig br-lan xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx::1/64
其中,IPv6地址是路由器WAN6自动获取到的地址的前4段。
之后是在 /etc/config/network 里删除 IPv6 ULA prefix。
然后打开 /etc/config/dhcp ,config dhcp ‘lan’ 里改成类似这样:
config dhcp 'lan'
option interface 'lan'
option start '100'
option limit '150'
option leasetime '12h'
option ra 'server'
option dhcpv6 'server'
option ra_management '1'
option ndp 'relay'
最重要的应该是 option ra ‘server’ 和 option dhcpv6 ‘server’ 两行。(改成server或者hybrid)
最后配置ip6tables。在 /etc/firewall.user 中加入
ip6tables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -s xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx::/64 -j MASQUERADE #其中的IP是LAN的前4段
然后重启路由器,应该就OK了。
相关参考:
1. OpenWRT配置IPv6的NAT(一般结合isatap使用):https://blog.blahgeek.com/2014/02/22/openwrt-ipv6-nat/
服务器是Windows的,现在的需求是通过一个CGI脚本输出一个pdf(或者是一个图片)。发现出来的文件的大小变大了,然后内容显示不出来或者乱码,估计是\r\n导致的问题。折腾了一下午,找到了答案。现在的代码如下:
filename = r'D:\example.pdf' #我这里要输出pdf print 'Content-type: application/pdf\n\n' import msvcrt msvcrt.setmode(1, os.O_BINARY) #使stdout为二进制 pdf_file = open(filename, 'rb') data = pdf_file.read() pdf_file.close() print data
20150626更新基于 linux kernel 4.0.6 的步骤,建议先看最后更新的部分
20151205更新,发现在8月13日时,来自4.2的mt7601u驱动被移植到了4.1.5,所以,升级内核到4.1.5或以上,只需要下载 mt7601u.bin 放到 /lib/firmware/ 下就可以了,就是执行下面这条命令。具体来源见 https://github.com/raspberrypi/linux/issues/1090
sudo wget https://github.com/porjo/mt7601/raw/master/src/mcu/bin/MT7601.bin -O /lib/firmware/mt7601u.bin
如果内核是4.1.5以上,下文都不需要看了,驱动已经自带,不需要自己编译,只需要补上 /lib/firmware/mt7601u.bin 就可以了。
否则,看下面的几行来更新系统,再补上 mt7601u.bin ,也就ok了。
20170107更新,最近把卡格了重新装raspbian系统,是2016-11-25的版本,内核是4.4,发现mt7601u.bin也已经自带,直接插上就用,不需要折腾。这个版本的蛋疼之处在于SSH默认关闭,需要在启动分区加上一个名为ssh的文件,才可以开启SSH。
首先,更新你的树莓派(避免编译出来版本不对导致不能insert):
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade sudo apt-get dist-upgrade sudo rpi-update
更新gcc和g++:
#可能有点问题,先不要更新 20150506 #sudo apt-get install gcc-4.8 g++-4.8 #sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-4.6 20 #sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-4.8 50 #sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/g++ g++ /usr/bin/g++-4.6 20 #sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/g++ g++ /usr/bin/g++-4.8 50
到MTK的官网下载驱动并传到树莓派上:http://www.mediatek.com/zh-CN/downloads/mt7601u-usb/
解压:
tar xjvf DPO_MT7601U_LinuxSTA_3.0.0.4_20130913.tar.bz2 cd DPO_MT7601U_LinuxSTA_3.0.0.4_20130913/
打开 common/rtusb_dev_id.c,在 {USB_DEVICE(0x148f,0×7601)}, /* MT 6370 */ 下面加入以下内容:
{USB_DEVICE(0x148f,0x760b)}, /* 360 Wifi */
{USB_DEVICE(0x2955,0x1001)}, /* baidu Wifi */
{USB_DEVICE(0x2a5f,0x1000)}, /* Tencent WiFi */
{USB_DEVICE(0x2955,0x0001)}, /* XiaoDu Wifi */
{USB_DEVICE(0x2717,0x4106)}, /* Xiaomi Wifi */
打开 include/os/rt_linux.h,找到
int fsuid; int fsgid;
并把它改为
kuid_t fsuid; kgid_t fsgid;
查看当前内核的版本:
uname -r
显示我的版本是3.18.8+ ,所以下载对应的3.18的linux源码,然后解压:
wget https://github.com/raspberrypi/linux/archive/rpi-3.18.y.tar.gz tar xvfz rpi-3.18.y.tar.gz
取得root权限,将源码移至/usr/src目录:
sudo su mv linux-rpi-3.18.y /usr/src
建立内核模块库目录的链接:
ln -s /usr/src/linux-rpi-3.18.y /lib/modules/3.18.8+/build cd /lib/modules/3.18.8+/build
make mrproper 可以看作更加强劲的 make clean 命令,用来清除环境变量,即清除配置文件,一般编译内核前都要运行:
make mrproper
将当前正在使用的系统的内核配置生成内核配置信息:
gzip -dc /proc/config.gz > .config
生成编译内核所需要的东西:
make modules_prepare
获取内核编译时生成的内核模块导出符号文件。因为不是从头编译内核,所以没有,但是编译内核模块需要这个:
wget https://github.com/raspberrypi/firmware/raw/master/extra/Module.symvers
再到网卡驱动目录中编译驱动(进入到DPO_MT7601U_LinuxSTA_3.0.0.4_20130913):
make make install modprobe mt7601Usta
如无报错,驱动就安装完成了。
之后是修改/etc/network/interfaces文件,我改成这样:
auto lo iface lo inet loopback iface eth0 inet dhcp allow-hotplug wlan0 iface wlan0 inet manual wpa-roam /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf iface default inet dhcp allow-hotplug ra0 iface ra0 inet manual wpa-roam /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
其中添加的ra0是对应MT7601的,wlan0没有改,插其他无线网卡应该也能正常用。
然后修改/etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf,填入要连接的无线网络的配置。
ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=netdev
update_config=1
network={
ssid="yourssid"
psk="yourpassword"
proto=RSN
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
pairwise=CCMP TKIP
group=CCMP TKIP
auth_alg=OPEN
priority=3
}
最后的priority是该配置的优先级,数字越大越先连接。添加几个就能在不同的地方自动连接了。
重启机器,用ifconfig、iwconfig等测试无线网卡能否正常工作。
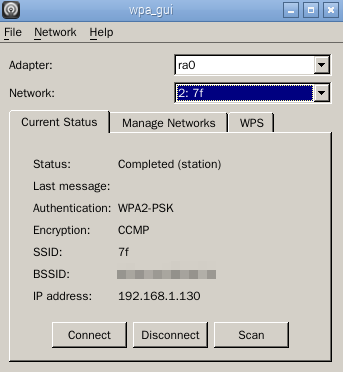
rdp远程登录进去,打开Wifi设置后的截图
=========================
20150306更新:在内核更新到3.18后,驱动需要重新编译,出现了种种问题,在参考了[2]和[3]后,升级了gcc版本和修改了rt_linux.h。
20150306于RaspberryPi Model B+测试成功,内核为3.18.8。
20150506更新:在升级gcc后,似乎在make modules_prepare时会遇到compiler too buggy的问题。我又找了一下,还是在树莓派的官方论坛,https://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?f=28&t=49864&start=179这里:
On the first time running rpi-source, you have to have the default gcc 4.6.3. You have to also specify –skip-gcc so that rpi-source doesn’t care about the different gcc in use and what’s been used to build the default kernel. If you run rpi-source with 4.8.2 as the default gcc, you’ll end up getting message like this during the kernel preparation (make prepare?) phase:
…error Your compiler is too buggy; it is known to miscompile kernels…
That’s why you have to first run rpi-source with the default gcc 4.6.3 with –skip-gcc parameter. After rpi-source gets all done, you have to change to gcc 4.8.2. The kernel doesn’t let you compile the kernel itself, but you can compile compatible modules for it. It’s bit tricky . It would be great if the default Raspbian gcc would compile compatible modules. Maybe gcc 4.8.3 would not complain about the kernel miscompile problem?
似乎是先用自带的4.6.3 prepare好了之后,再换用4.8的意思,各位研究一下吧。
20150623更新:在https://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?f=28&t=49864&start=353找到了一个适用于3.18.11+ #776的驱动,传到了百度盘,使用方法:
tar xzf mt7601-3.18.11-776.tar.gz /install.sh
另外,在github上有了第三方的驱动,适用于kernel 3.19以上的版本,并且被合并到kernel 4.2,所以未来升级到4.2的时候就再也不用烦恼了。如果要自己编译,就到上面的github链接看看吧。
今天把我的RPi B+更新到了4.0.6内核,(Linux raspberrypi 4.0.6+ #798 PREEMPT Tue Jun 23 17:48:03 BST 2015 armv6l),然后成功使用了上文提到的github的新驱动。
步骤与之前的基本相同。以下步骤未详细说明的都在本文中有提及。
相关参考:
1.在树莓派上使用360WIFI(也适用于小米、百度、腾讯WIFI):http://shumeipai.nxez.com/2014/12/07/raspberry-pi-use-360wifi.html
2.http://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?f=28&t=98913
3.http://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?f=28&t=49864&p=690479

先上图。最近我正要搭建一个类似上图的网络,我要从图中的LAN Host 1通过wifi访问图中的WLAN Client,其中两个无线路由器都运行OpenWrt。后来我找到了这篇文章。从中发现了来自OpenWrt Wiki的方法(上图也是取自此wiki),正好解决了这个问题。
在上一篇文章中,我们通过ddns-scripts和一个外部的.php文件,实现了dnspod上的ipv4的ddns功能。
最近有了ipv6的ddns的需求,于是在上文的基础上小改了一下,现在dnspod上的ipv6的ddns也没问题了。
1.在上一篇文章的基础上,修改了一下dnspodupdate.php中的“’record_type’=>’A”为“’record_type’=>’AAAA’”,也可以直接下载:dnspodupdate6.zip,并上传到一个外网的空间上。
2.修改路由器里的/usr/lib/ddns/dynamic_dns_functions.sh,把位于约75行的
current_ip=$(ifconfig $ip_interface | grep -o 'inet addr:[0-9.]*' | grep -o "$ip_regex")
改为
current_ip=$(ifconfig $ip_interface | grep 'Global' | grep -o 'addr: [0-9a-f:]*' | cut -c7-) #我的grep和cut是现学现卖的,有没有更好的写法?
不过这样一来,以“接口”来获取ip的就只能获取ipv6的地址了,如果要获取ipv4的地址,“”就选“网络”吧。
3.打开/usr/lib/ddns/services,添加一行
"dnspod.com_ipv6" "http://www.xxxxx.com/api/dnspodupdate6.php?username=[USERNAME]&password=[PASSWORD]&domain=[DOMAIN]&myip=[IP]" #注意这里的http://www.xxxxx.com/要改
4.更改/etc/config/ddns的配置,service_name选dnspod.com_ipv6,再填上各种参数,这样就完成了~
opkg update opkg install openvpn openvpn-easy-rsa #easy-rsa不一定要安装,我把easy-rsa的操作在PC上进行
[important]下面的操作在Windows上进行,请先下载并安装Windows版的OpenVPN。如果你打算在路由上使用easy-rsa,对应的操作见文末参考来源的①和④[/important]
set KEY_COUNTRY=CN
set KEY_PROVINCE=Guangdong
set KEY_CITY=Guangzhou
set KEY_ORG=7forz
set KEY_EMAIL=7f@7forz.com
set KEY_CN=7forz
set KEY_NAME=7forz
set KEY_OU=7forz
set PKCS11_MODULE_PATH=7forz.com
set PKCS11_PIN=1234
init-config
vars
clean-all
build-ca (创建根证书)
Country Name (2 letter code) [CN]:
State or Province Name (full name) [Guangdong]:
Locality Name (eg, city) [Guangzhou]:
Organization Name (eg, company) [7forz]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [7forz]:
Common Name (eg, your name or your server’s hostname) [7forz]:
Name [7forz]:
Email Address [7f@7forz.com]:
build-dh
build-key-server server (服务器证书,server为机器名)
Country Name (2 letter code) [CN]:
State or Province Name (full name) [Guangdong]:
Locality Name (eg, city) [Guangzhou]:
Organization Name (eg, company) [7forz]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [7forz]:
Common Name (eg, your name or your server’s hostname) [7forz]:
Name [7forz]:
Email Address [7f@7forz.com]:
Please enter the following ‘extra’ attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:password
An optional company name []:
build-key client1 (创建客户端证书,client1为用户名,之后还可以创建client2,client3)
Country Name (2 letter code) [CN]:
State or Province Name (full name) [Guangdong]:
Locality Name (eg, city) [Guangzhou]:
Organization Name (eg, company) [7forz]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [7forz]:
Common Name (eg, your name or your server’s hostname) [7forz]:
Name [7forz]:
Email Address [7f@7forz.com]:
Please enter the following ‘extra’ attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:password
An optional company name []:
如果出现
failed to update database
TXT_DB error number 2
错误,貌似是因为Common Name相同而导致的,请在生成时修改之或者打开keys\index.txt并清除其中内容,再执行一次build-key client1命令
之后把 ca.crt server.* dh*.pem 传到路由的 /etc/openvpn 目录下
再把 ca.crt client*.* 放到你电脑的 OpenVPN\config 目录下